Casting and forging are two common manufacturing processes in metalworking that differ significantly in their principles, applications and characteristics.
What is Casting?
Casting is a manufacturing process where a liquid material, typically molten metal, is poured into a mold or cavity and allowed to cool and solidify. The solidified part is then ejected or broken out of the mold to create the final product. Here are the key aspects of casting.
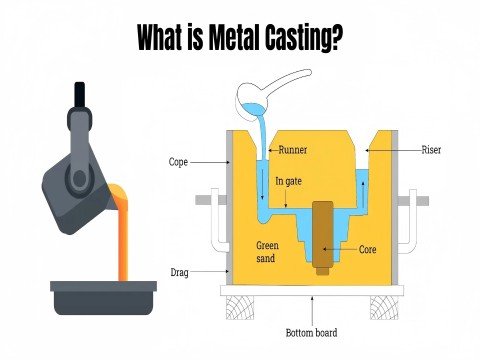
Process:
- Metal is heated to its melting point and then poured into a mold.
- The mold can be made from various materials, such as sand, metal, or ceramic.
- The liquid metal fills the mold cavity and takes its shape as it cools.
Advantages:
Complex Shapes: Casting can produce intricate and complex shapes, including parts with internal cavities.
Material Flexibility: It supports a wide range of alloys and materials.
Economical: Lower initial tooling costs and reusable molds make it cost-effective for small to large production runs.
Applications:
Ideal for large components and parts requiring detailed designs, such as engine blocks, turbines, and medical implants.
What is Forging?
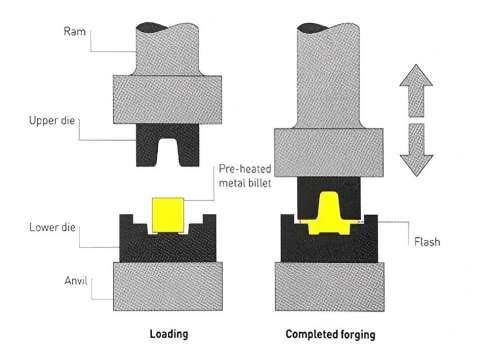
Forging is a manufacturing process that shapes metal by applying compressive forces using tools such as hammers or presses. The metal is usually heated to make it more malleable but remains in a solid state during the process.
Process:
- Metal is heated to a specific temperature (usually below its melting point) and then shaped using compressive forces.
- Common methods include hot forging (above the recrystallization point) and cold forging (at or near room temperature).
Advantages:
Strength: Forging aligns the metal’s grain structure, resulting in superior mechanical properties, including higher tensile and fatigue strength.
Durability: Minimizes internal voids and defects, leading to high structural integrity.
Material Efficiency: Reduces material waste and scrap.
Applications:
Suitable for components requiring high strength and durability, such as crankshafts, gears, and aerospace parts.
Casting is ideal for complex shapes, large components, and a wide range of materials, but it may have lower strength and higher defect risks.
Forging excels in producing strong, durable parts with superior mechanical properties but is limited in design complexity and can be more expensive.
Haichen die casting manufacturer
Haichen is a well-known manufacturer specializing in die casting and related manufacturing services. We mainly supply cold chamber and hot chamber die casting machines and auxiliary equipments. They provide high-quality die-cast components for various industries, including automotive, electronics, home appliances, and industrial equipment.


Key Features of Haichen Die Casting
Materials:
They work with a variety of materials, including aluminum die casting, zinc die casting, and magnesium die casting, depending on the application requirements.
Industries Served
Automotive: Engine components, transmission parts, brackets, and housings.
Electronics: Heat sinks, connectors, and enclosures.
Home Appliances: Parts for refrigerators, washing machines, and air conditioners.
Industrial Equipment: Machinery components and structural parts.
Global Reach
Haichen serves clients worldwide, offering competitive pricing and reliable delivery schedules.
Sustainability
We focus on eco-friendly manufacturing processes, including recycling of materials and reducing waste.
Why Choose Haichen?
Expertise: Decades of experience in die casting and manufacturing.
Customization: Ability to tailor solutions to meet specific customer requirements.
Cost-Effective: Efficient production processes and economies of scale.
Reliability: Consistent quality and on-time delivery.
If there is any demand, welcome to consult us.



