In die casting, the mould (called a die) must withstand high temperatures, pressure, and repeated cycles. The Die casting Mould material used are high-performance metals designed for durability, thermal stability, and wear resistance.
The die-casting mold consists of two parts, separated according to the product’s draft angle. Molten metal is poured in from the fixed end, and the die-casting part solidifies upon cooling. The die-casting part remains on the movable side, which is ejected by ejector pins. After removing the die-casting part, we recommend applying lubricant to the mold using a spraying machine.
Designing and manufacturing die-casting molds requires expertise and skills in mold making, metallurgy, and engineering. The quality of the mold significantly impacts the quality, consistency, efficiency, and overall production cost of the die-casting process. Therefore, selecting the appropriate mold material is crucial for the success of the die-casting process.

Primary Die casting Mould material
- Tool Steels
- Maraging Steel
- Copper Alloys
- Hot Work Steels
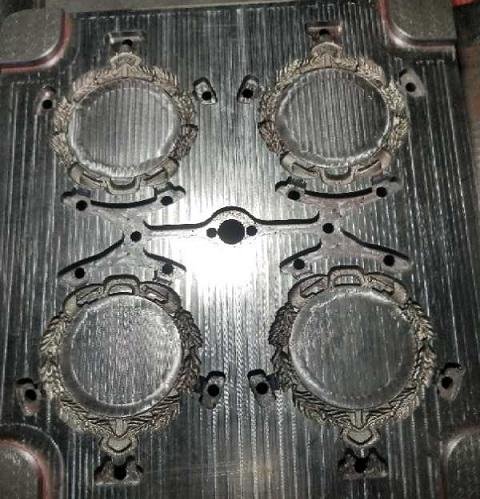

- Tool Steels (Most Common)
- H13 (AISI/SAE):
- Composition: Chromium, molybdenum, vanadium.
- Properties: Excellent thermal fatigue resistance, high hardness, and good thermal conductivity.
- Applications: Aluminium, magnesium, and zinc alloy die casting.
- Lifespan: ~100,000 to 1,000,000 cycles, depending on cooling and maintenance.
- H11 (AISI/SAE):
- Similar to H13 but with slightly lower toughness. Used for smaller or less complex dies.
- DIN 1.2344 (European Standard):
- Equivalent to H13, widely used in Europe.
- H13 (AISI/SAE):
- Maraging Steel
- Composition: Nickel, cobalt, molybdenum.
- Properties: Ultra-high strength, excellent dimensional stability, and resistance to cracking.
- Applications: High-pressure dies for complex parts (e.g., automotive components).
- Copper Alloys (for Inserts)
- Composition: Copper with beryllium, chromium, or tungsten.
- Properties: Superior thermal conductivity for rapid cooling.
- Applications: Inserts in critical areas (e.g., around cores or thin walls) to reduce cycle time.
- Hot Work Steels (e.g., DIN 1.2714):
- Used for high-stress components like ejector pins or cores.

Key Requirements for Die casting Mould material
- Thermal Fatigue Resistance: To handle repeated heating/cooling cycles (critical for aluminium/magnesium casting at 600–700°C).
- Wear Resistance: To endure abrasive molten metal flow.
- High Hardness: Maintains shape under high clamping pressures (up to 2,000+ bar).
- Machinability: Allows precise die cavity shaping.
Surface Treatments

To enhance performance:
- Nitriding: Creates a hard, wear-resistant surface layer.
- Coatings (e.g., TiN, CrN): Improve corrosion resistance and reduce soldering (metal sticking to the die).
Die casting Mould material Selection Factors
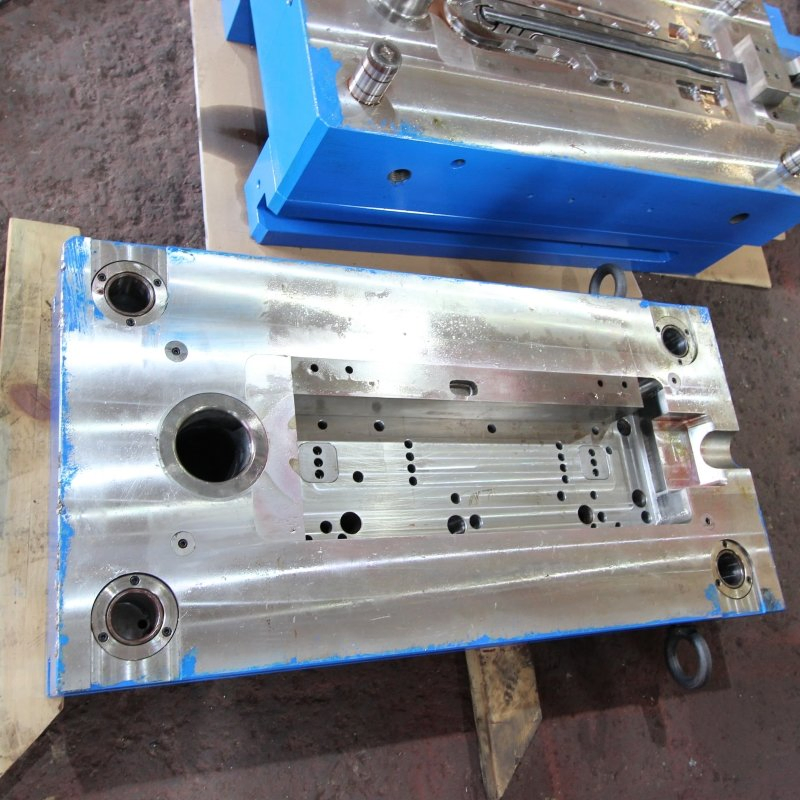

- Cast Metal
- Production Volume
- Part Complexity
- Cast Metal:
- Aluminium/Magnesium: Require H13 or maraging steel (high melting points, ~600–700°C).
- Zinc: Softer alloys allow use of lower-cost steels (e.g., P20).
- Production Volume:
- High-volume runs (millions of cycles) demand premium steels (H13 with coatings).
- Part Complexity:
- Complex geometries need tougher steels to prevent cracking.
Typical Die Lifespan
| Cast Metal | Die Material | Lifespan (Cycles) |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc | H11/P20 | 1,000,000+ |
| Aluminium | H13 (Nitrided) | 150,000–500,000 |
| Magnesium | H13/Maraging | 100,000–300,000 |
Applications
- Automotive: Engine blocks, transmission housings (H13 steel).
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphone frames (zinc dies with P20 steel).
- Aerospace: Lightweight magnesium components (maraging steel).
Advantages of Die Casting Moulds
- Reusable for high-volume production.
- Deliver tight tolerances (±0.1 mm) and smooth surfaces.
- Minimize post-processing compared to sand or investment casting.
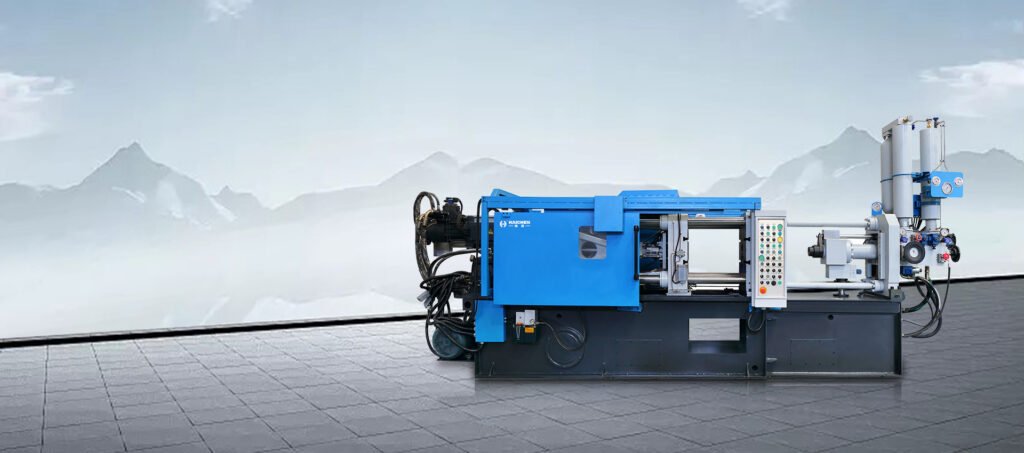
Haichen die casting mould
Haichen Die Casting Mold Design and Applications: Key Features
Based on comprehensive analysis of multiple sources, Haichen’s die casting mold technology exhibits the following characteristics:
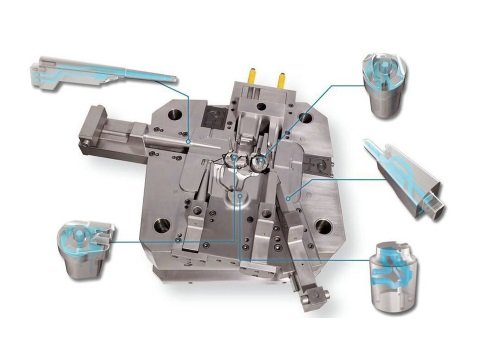
- Flexible Mold Configurations
- Standardization & Precision Engineering
- Material Compatibility
- End-to-End Solutions
- Mold Maintenance & Lifespan
- Real-World Applications
- Certifications & Quality Control
- Mold Size Range
Flexible Mold Configurations
- Haichen’s cold chamber die casting machines support single or dual cavity molds, enabling users to adapt to production needs (e.g., radiators, automotive parts). This flexibility suits scenarios requiring high-volume production or diverse product types.
Standardization & Precision Engineering
- Mold designs comply with Chinese mechanical industry standards (JB/T series) and EU CE safety regulations, ensuring structural integrity. Critical components are optimized via Finite Element Analysis (FEA) to enhance durability and dimensional accuracy.
- The cold chamber machines use magnetic encoder-controlled injection positioning, with PLC-managed four-stage injection (slow, first fast, second fast, intensification), minimizing molten metal turbulence and reducing mold wear.
Material Compatibility
- Cold chamber machines handle aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys (high melting points), requiring molds with heat-resistant designs. Example: Aluminum radiator molds enable single-piece casting for improved thermal efficiency.
- Hot chamber machines specialize in zinc and lead alloys (low melting points), featuring integrated mold-furnace designs (e.g., gooseneck structures) to shorten metal flow paths and enhance fill efficiency.

End-to-End Solutions
- Haichen offers full-process services, from mold design to machine configuration, including Mold Flow Analysis and process optimization. Example: Precision zinc alloy lock cores and door handles achieve lightweight yet robust designs.
- Multilingual control systems (Chinese, English, Russian, etc.) simplify global operation and parameter adjustments.
Mold Maintenance & Lifespan
- Hydraulic systems integrate European/American components (e.g., Vickers, Rexroth) for stability, reducing mold damage from pressure fluctuations.
- Smart lubrication systems: Centralized lubrication every 500–700 cycles; manual lubrication points serviced biweekly (first 6 months) and monthly thereafter.
Real-World Applications
- Aluminum cookware molds: Achieve uniform thick-walled casting for heat resistance.
- LED housing molds: Optimized for heat dissipation with automated part removal.
- Zinc alloy medal molds: Support intricate polishing/plating processes (final thickness: 1.3–1.4 mm).
Certifications & Quality Control
- Molds meet ISO 9001 and CE certifications, complying with GB/T 21269-2023 standards. Critical tolerances: Dynamic platen parallelism ≤0.12 mm.
Mold Size Range
- Cold chamber machines accommodate mold thicknesses from 200–580 mm (200-ton models) to 400–950 mm (880-ton models), catering to diverse product dimensions.
Summary: Haichen’s die casting molds excel in precision engineering, material adaptability, and intelligent maintenance, synergizing with high-ejection-control machines and stable hydraulics. These capabilities serve automotive, appliance, and hardware industries with robust, high-quality production outcomes.

Die materials are a critical investment, balancing upfront cost with long-term durability and part quality.



