Die casting heating bush cost analysis includes material cost, mold cost, production cost, post-processing costs and so on.
The die-casting cost of the heating sleeve will affect by many factors. Such as materials, molds, production efficiency and post-processing. The die-casting cost of the heating sleeve can be effectively reduced by optimizing the design, selecting suitable materials and improving production efficiency.
We will discuss heating bush cost analysis in die casting from
- Material cost
- Mold cost
- Production cost
- Post-processing costs
- Optimization strategy
The cost analysis of heating bushes involves many aspects, including material cost, mold cost, production cost, and post-processing cost. The following is a detailed description of the cost analysis of heating bushes in die casting:
Material cost
Material cost is an important part of die casting cost, usually accounting for 10%-20% of the total cost. For die casting parts such as heating sleeves, the material selection directly affects the cost.
For example, aluminum and magnesium often use in die casting. Due to their high melting point and good fluidity. But the price of these materials is high, especially aluminum, which may cost more than $4 per kilogram.
In addition, if rare or special materials are used, the cost may increase further.

Common Materials and Densities
- Copper alloys (e.g., CuAl10Fe5Ni5Cr): Density approximately 8.86 g/cm³
- Ordinary steel (tool steel): Density approximately 7.8 g/cm³
- Aluminum bronze (Al-Bronze): Density approximately 8.5 g/cm³ (typical value, commonly used in the industry)
Weight Estimation
- Copper Alloy: 39.3 cm³ × 8.86 g/cm³ ≈ 348 g
- Steel: 39.3 cm³ × 7.8 g/cm³ ≈ 307 g
- Aluminum Bronze: 39.3 cm³ × 8.5 g/cm³ ≈ 334 g
Material Unit Prices
(2024-2025 Market Reference)
Copper: Approximately 8 USD/kg (based on the recent LME price range of 2,500-9,000 USD/t)
Steel: Approximately 0.8 USD/kg (ordinary carbon tool steel)
Aluminum Bronze: Approximately 9 USD/kg (surcharge for copper-based alloys)
Cost Considerations
- Copper alloys offer the best thermal conductivity but have the highest material cost.
- Steel offers the lowest cost, but its thermal conductivity is only approximately 45 W/m·K, making it suitable for applications where thermal efficiency is not a priority.
- Aluminum bronze offers a balance between thermal conductivity and wear resistance, and its cost is slightly higher than copper alloys.

Mold Cost
The mold is the core of the die casting process. And its cost usually accounts for 10%-20% of the total cost of the die casting.The design complexity, size and precision of the mold directly affect the cost of the mold.
Haichen die casting mold
Haichen with rich experience of producing die casting molds. For example, aluminium alloy pan molds.
Key advantages include high production speeds, minimal material waste, and the ability to integrate reinforced structures and intricate surface details directly into the casting, ensuring both functional excellence and aesthetic appeal in every piece.
Haichen die casting machine company can also produce replaceable pot bottom moulds for same diameter with different bottom shape pans. That can help save and reduce customer’s significant cost.

The initial investment in the mold may be as high as tens of thousands of dollars. But in the long run, high production volume can dilute the mold cost.
Heating bush cost structure
- Heating element (ceramic/resistance heating mantle)
- Insulation material
- Electrical wiring and connectors
- Temperature control system (temperature sensor + controller)
Mold Material and Structure
Using an aluminum alloy mold (such as zinc alloy casting) can reduce mold base costs by approximately 50%, thereby relatively increasing the proportion of the heating sleeve in the overall cost.
Preheating Temperature Requirements
For thick-walled sleeves such as automotive bearings, the typical preheating temperature is between 150 and 200°C, which determines the heating power and insulation material selection.
Production Batch and Number of Cavities
While the base cost of multi-cavity molds increases, the unit cost of the heating sleeve remains essentially unchanged. Therefore, the proportion of the heating sleeve decreases further in large-scale production.

Production cost
Production cost include equipment depreciation, energy consumption, and labor costs. The hourly rate and cycle time of the die casting machine are key factors in calculating production costs.
Processing and Manufacturing Costs
Precision machining
Turning, milling, drilling, and other processes, with machine costs approximately 300-500 CNY/hour.
Heat treatment/brazing
Improves heat resistance, costs approximately 100-200 CNY/unit.
Quality inspection
Thermal imaging, thermal resistance measurement, etc., costs approximately 50-100 CNY/unit.

Post-processing costs
Die castings often require post-processing operations such as deburring, cleaning and polishing.
These operations can add additional costs, especially for heating jackets with complex shapes, which may require more post-processing steps.

Optimization strategy
In order to reduce the die casting cost of heating sleeves, we can take the following measures:
Optimize mold design
Reduce mold costs by reducing the complexity and weight of the mold.
Choose suitable materials
Select cost-effective materials according to the specific requirements of the heating sleeve, and avoid using high-cost rare materials.
Improve production efficiency
Reduce labor and energy costs through automation and optimization of production processes.
Use JIT methods
reduce inventory and raw material waste through just-in-time production, thereby reducing overall costs.
Haichen die casting machine
Haichen is one Chinese die casting machine manufacturer for more than 10years. At the same time, we produce both high pressure cold chamber die casting machine , hot chamber die casting machine and spare parts. They have durable and highly precise features.
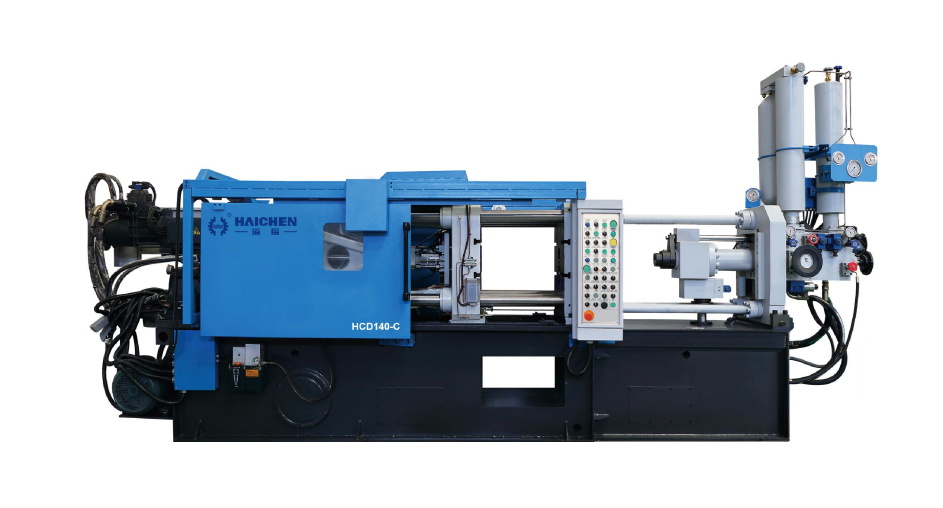


Haichen also produce die casting machine auxiliary equipment. Such as conveyor, vacuum machine, mold temperature controller, industrial robot, sprayer and so on.

We supply cold chamber and hot chamber die casting machine spare parts.
Welcome contact us.



